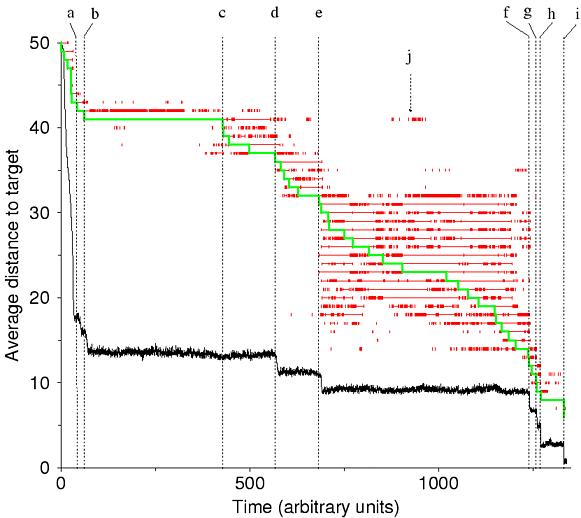

This is Figure 1A of our report showing a simulation of an RNA population evolving towards a tRNA target shape in a flow reactor logistically constrained to a capacity of 1,000 sequences on average. The replication accuracy per position is 0.999. The replication rate (=fitness) of a sequence whose shape is alpha is given by 1 / (0.01 + d(alpha,tRNA)/l), where l=76 is the sequence length and d the distance between alpha and the target. Linear or exponential functions did not affect the character of the dynamics. The initial population consisted of 1,000 identical sequences folding into a random shape. The target was reached after approximately 11x10^6 replications. The black trace shows the average structure distance of the shapes in the population to the target. The chain of shape innovations linking the initial shape to the target (evolutionary path) comprises 43 shapes (excluding both initial and target shape). To each of these corresponds one horizontal level placed above the black curve. The topmost (bottom) level belongs to the initial (target) shape. For these levels only the time axis has a meaning. At each level a series of red intervals represents the time periods during which the corresponding shape was present in the population. The green step curve indicates the transitions between shapes, and hence the time spent by each shape on the evolutionary path. on a green step to view the shape associated with it on the left. Each transition was caused by a single point mutation in the underlying sequences. The dotted lines mark transitions corresponding to the arrows in the chain of shape innovations. on the label of a dotted line for a discussion of the transition.
A continuous transition from a shape alpha to a shape beta can be recognized by the fact that beta is present (red trace) intermittently, yet consistently, in the population well before becoming a link in the evolutionary path (green trace). In other words, beta's presence is stochastically correlated with that of alpha, because it is near alpha in shape space. In contrast, a discontinuous transition from beta to gamma is characterized by the fact that gamma's presence does not correlate with beta's (mutants of sequences folding into beta don't typically fold into gamma).